teaching_web_development
Introduction to PHP
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a popular server-side scripting language designed for web development but also used as a general-purpose programming language.
It is especially suited for creating dynamic web pages and applications.
Resources
Slides
Features
- Inspired by C and Perl
- Loosely typed language
- Supports Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Extends HTML capabilities
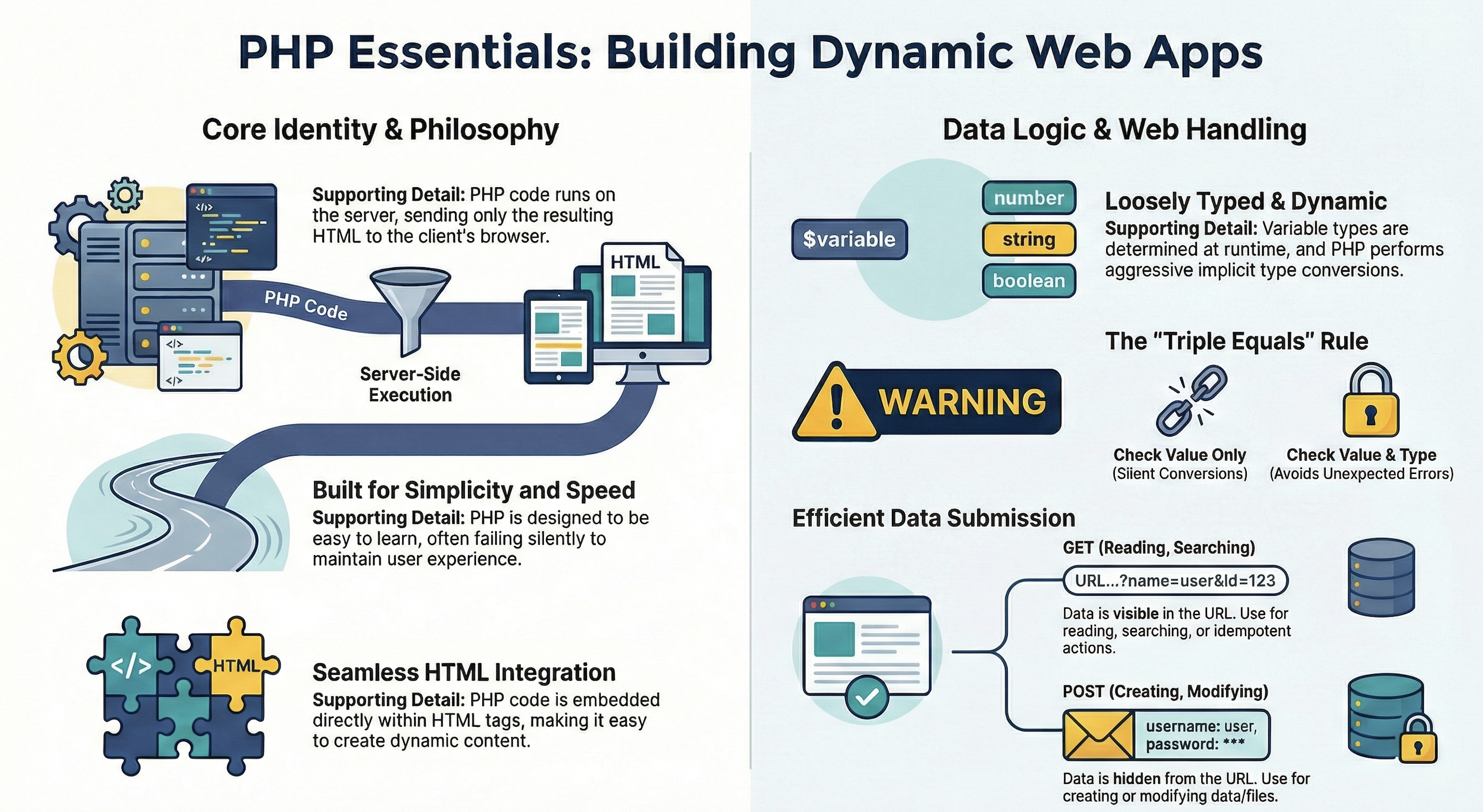
Philosophy of PHP
- PHP is designed to be easy to learn and use
- It emphasizes simplicity and speed
- Not an exercise in building the most elegant or consistent language possible
- Errors fail silently by default to avoid disrupting the user experience
- If you make mistakes, you are responsible for finding and fixing them
Key Features of PHP
- Server-Side Scripting: PHP code is executed on the server, generating HTML that is sent to the client’s browser.
- Embedded in HTML: PHP can be embedded directly within HTML code, making it easy to create dynamic web content.
- Database Integration: PHP has built-in support for various databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite, allowing for dynamic data-driven applications.
- Cross-Platform: PHP runs on various platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, making it versatile for different server environments.
- Open Source: PHP is free to use and has a large community that contributes to its development and provides support.
Example PHP Code
- Interleaved HTML and PHP code:
<h1> Hello from HTML </h1>
<?php
// This is a simple PHP script that outputs "Hello, World!"
echo "Hello, World!";
?>
<p> This is more HTML content. </p>
- The output of the above code will be:
Hello from HTML
Hello, World!
This is more HTML content.
-
🚀 Concept: Output from PHP is substituted into the HTML at the location of the PHP code.
-
🚀 Concept: It runs on the server, and the client only sees the resulting HTML.
Getting Started with PHP
-
Start MAMP on your machine.
_ Click on “Start” to start the Apache server.
- Navigate to
http://localhost:8888orhttp://localhost:8888/MAMP/?language=Englishin your web browser to verify that the server is running.
Configuring PHP
-
Edit the file
php.inito configure PHP settings. -
On my Mac OS X, the file is located at:
/Applications/MAMP/bin/php/php8.3.28/conf/php.ini -
The contents of
php.inilook like this:; PHP's initialization file, generally called php.ini, is responsible for ; configuring many of the aspects of PHP's behavior. ; ; This file is divided into sections, each section having directives that ; configure various aspects of PHP's behavior. Each directive is explained ; via comments in this file. ; ; For more information about setting up PHP, please refer to the ; documentation at https://www.php.net/manual/en/configuration.file.php -
Start writing PHP code in your web server’s document root directory (e.g.,
htdocsfor MAMP). -
On my Mac OS X, the document root directory is located at:
/Applications/MAMP/htdocs -
In this directory, create a new folder named
my_php_site. -
In this folder, create a file with a
.phpextension (e.g.,index.php) to start writing your PHP code. -
Open your favorite code editor (e.g., VS Code, vi, Sublime Text, or any text editor) to write PHP code.
-
Write the PHP code in the
.phpfile you created.
<?php
// Your PHP code goes here
echo "Hello World!";
?>
- Navigate to
http://localhost:8888/my_php_site/index.phpin your web browser to see the output of your PHP code.
PHP Script
-
A PHP script is typically enclosed within
<?phpand?>tags. -
A PHP file usually has a
.phpextension. -
A PHP script can generate HTML content dynamically.
Syntax Basics
-
PHP is loosely typed, meaning you do not need to declare variable types explicitly.
-
Static typing can be found in C++ or Java, where you must declare the type of a variable before using it.
-
Dynamic typing means that the type is determined at runtime based on the value assigned to the variable.
-
For example:
<?php
$age = 25; // $age is an integer
$name = "Alice"; // $name is a string
$price = 19.99; // $price is a float
?>
📝 Examples
-
Example code snippets:
<?php
// Example 1: Variables and Output
$name = "John";
echo "Hello, " . $name . "!"; // Outputs: Hello, John!
?>
<?php
// Example 2: Conditional Statements
$age = 20;
if ($age >= 18) {
echo "You are an adult.";
} else {
echo "You are a minor.";
}
?>
<?php
// Example 3: Looping
for ($i = 1; $i <= 5; $i++) {
echo "Number: " . $i . "<br>";
}
?>
<?php
// Example 4: Functions
function greet($name) {
return "Hello, " . $name . "!";
}
echo greet("Alice"); // Outputs: Hello, Alice!
?>
<?php
// Example 5: Arrays
$fruits = array("Apple", "Banana", "Cherry");
foreach ($fruits as $fruit) {
echo $fruit . "<br>";
}
?>
Implicit type conversions
- ⚠️ PHP performs implicit type conversions when necessary.
- For example, when a string is used in a numeric context, PHP will attempt to convert it to a number.
<?php
$number = "10"; // string
$sum = $number + 5; // PHP converts $number to an integer
echo $sum; // Outputs: 15
?>
- ⚠️ Be cautious with implicit conversions, as they can lead to unexpected results.
Operators
- PHP supports various operators for arithmetic, comparison, logical operations, and more.
- Examples of operators:
<?php
$a = 10;
$b = 5;
$sum = $a + $b; // Addition
$difference = $a - $b; // Subtraction
$product = $a * $b; // Multiplication
$quotient = $a / $b; // Division
$isEqual = ($a == $b); // Comparison
$isGreater = ($a > $b); // Comparison
$andCondition = ($a > 5 && $b < 10); // Logical AND
$orCondition = ($a < 5 || $b < 10); // Logical OR
?>
- == will perform type conversion if the types of the operands are different.
- === will not perform type conversion and will check both value and type.
- 🚀 NOTE: = is the assignment operator.
Increment and Decrement Operators
- PHP provides increment (
++) and decrement (--) operators to increase or decrease the value of a variable by one.<?php $x = 5; $x++; // Increment: $x is now 6 $y = 10; $y--; // Decrement: $y is now 9 ?> - These operators can be used in both prefix and postfix forms.
<?php $a = 3; $b = ++$a; // Prefix: $a is incremented to 4, then assigned to $b $c = $a++; // Postfix: $c is assigned the value 4, then $a is incremented to 5 ?> - The prefix form increments or decrements the variable before its value is used in an expression, while the postfix form uses the variable’s current value before incrementing or decrementing it.
🎮 Fun Activity
- What values will be printed by the following code?
<?php
$x = 12;
$y = 15 + $x++;
echo "x is $x and y is $y";
$z = 20 + ++$x;
echo "x is $x and y is $y and z is $z";
?>
String concatenation
-
The . (dot) operator is used for string concatenation
-
🤔 Remember: The + (plus) operator will try to aggeressively type convert and add
-
Example code below:
<?php
$a = "Hello " . "World";
echo $a . "\n";
?>
Side effect assignment
-
⚠️ NOTE This is not a good practice
-
Use them sparingly but I show them for the sake of completeness
-
Try the following code in the online PHP compiler
<?php
$x = 10;
$x += 2;
echo $x;
?>
Type casting
-
PHP does aggressive type casting
-
Floating point
<?php
$x = 56;
$y = 12;
echo $x / $y;
?>
Activities: 🎮
- What will be the output of the following code?
<?php
$z = "100" + 36.25 + TRUE;
echo $z;
?>
-
Explicit type casting
-
🛠️ What will be the output of this code?
<?php
echo "100" + (string) 10;
?>
- 💡 What will be the output of this code?
<?php
echo "100" . string(10)
?>
- And this?
<?php
echo (int) 9.9 - 1.9;
?>
- What about this?
<?php
echo "Soumya" . 25;
?>
- And this one?
<?php
echo "Soumya" + 25;
?>
-
Concept 🚀 ⚠️ There are no errors! Only silent type conversion. Beware!
-
Concept 🚀 ⚠️
FALSEandNULLbecome 0 andTRUEbecomes 1.- Use ===
-
Concept 🚀 ⚠️
echodoes not showFALSE(since it becomes 0)
Equality vs. Identity
- Difference between
==and===
<?php
if (123 == "123") print ("Equal \n");
if (123 === "123") print ("Equal \n");
?>
-
More fun examples in the video by Dr. Chuck Severance on equality
-
==Aggressively convert/cast its operands
Function return values
-
If a function fails, it can return
FALSE! -
e.g.
strpos()returnFALSEif it did not find anything.FALSEcan get converted to 0! -
🚀 ⚠️ Concept Hence use
===to check ifstrpos()found the value or not
Comments
- two kinds
<?php /* comment .... */ # comment ?>
Diagrammatic summary of PHP basics
🛠️ Interview with PHP creator
Arrays
-
Use
arraykeyword
<?php
$str_array = array("Hello", "World");
echo $str_array[1];
?>
Array functions
-
array functions
??(exists),count,sort(sort by values in place),ksort(sort by keys),asort(sort by values) -
print_r(print array),explode(split array by delimiter) -
💡
$_GET(all constituents of end of URL)
Functions
-
call by value (default)
-
call by reference (use
&) -
globalvariables -
include
<?php
include "header.php";
?>
Form processing in PHP
-
PHP can be used to submit data from forms
-
If using GET, variables saved in
$_GET -
If using POST, variables saved in
$_POST -
Video comparing GET vs POST and how variables transferred from client to server
-
GET is used when you are reading or searching
-
POST is used when data is being created or modified
-
🧩 🚀 Concept: GET URLs should be
idempotent. If you hit refresh, you should get same result. For example, you are searching for a part numberURL?partid=890 -
Search engines also follow URLs (so if your URL has a GET request and it is modifying data, then ….. :-)
-
GET has an upper limit on the number of bytes you can send
-
Video outlining different PHP form elements (radio boxes, etc)
🎮 Practical for PHP forms
- Code example:
<p> Forms in PHP</p>
<form method="post">
<label>Input guess</label>
<input type="text" name="guess" id="guess"/>
<input type="submit">
</form>
- All this gets saved in
$_POST
<?php
print_r($_POST)
?>
-
🚀 Concept:
$_POSThas all the information in an array.guess(from the name tag in input field) will have the value. -
🚀 Concept: If you use
POSTthe information will not show up in the URL.
🎮 Full code
-
Save the following in
form1.php. -
On My Mac OS X, this is saved in the folder ` /Applications/MAMP/htdocs/my_php_site`
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
$txt = "PHP";
echo "I love $txt!";
?>
<p> Forms in PHP</p>
<form method="post">
<label>Input guess</label>
<input type="text" name="guess" id="guess"/>
<input type="submit">
</form>
<pre>
<?php
print_r($_POST)
?>
</pre>
</body>
</html>
- Start
MAMPand go to the following http://localhost:8888/my_php_site/form1.php
Other input types in forms
-
Radio buttons
-
Check boxes
-
Dropdown